Thirsty Giants: The Hidden Water Footprint of Data Centers
Explore how modern data centers consume massive amounts of water for cooling, the environmental impact, and innovative solutions for sustainable operations in the tech industry.
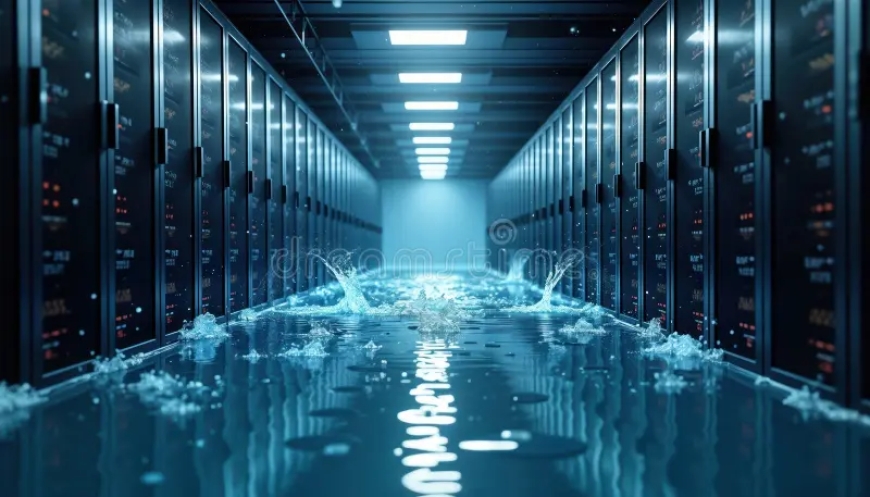

As the world becomes increasingly digital, data centers—the backbone of cloud computing, AI, and online services—are expanding at an unprecedented rate. While much attention is given to their electricity consumption, one often overlooked resource is water. Modern data centers rely heavily on water for cooling systems to maintain optimal operating temperatures, and the scale of consumption can be staggering.
Estimates suggest that a single large data center can use millions of gallons of water annually, especially those using evaporative cooling systems. This consumption puts pressure on local water supplies, particularly in water-stressed regions, raising concerns about environmental sustainability and resource management.
Why Water Is Critical for Data Centers
Cooling is essential for data centers because servers generate tremendous heat. Many facilities use water-cooled chillers or evaporative cooling towers because water is highly efficient at heat transfer compared to air-based systems. However, this efficiency comes at the cost of high water usage, making water scarcity a serious issue in areas hosting large tech hubs.
The environmental impact isn’t limited to water consumption alone. Evaporative cooling can affect local ecosystems, increase energy requirements for water treatment, and exacerbate competition with agricultural and residential water needs.
Innovative Solutions and Sustainable Practices
Leading tech companies are now seeking water-efficient alternatives to reduce their environmental footprint:
Air-based and hybrid cooling systems—reduce reliance on water while maintaining server efficiency.
Water recycling and reuse—capturing and reusing cooling water to minimize freshwater intake.
Locating data centers near abundant water sources or in cooler climates—natural temperature and water advantages lower overall consumption.
AI-driven cooling optimization—smart systems that adjust cooling in real-time to reduce unnecessary water use.
Companies like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon have already started implementing some of these measures, with a focus on achieving carbon-neutral and water-neutral operations.
As global demand for cloud computing, AI, and digital services continues to grow, the challenge of balancing technology growth with sustainable water use will intensify. Policymakers, industry leaders, and communities must collaborate to ensure that data centers remain technologically advanced but environmentally responsible, minimizing their water footprint while meeting the world’s insatiable digital appetite.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0