How US Strategic Maneuvering Is Straining India–China Relations: A Beijing Perspective
An analytical perspective from Beijing on how US strategic and military ambitions in the Indo-Pacific are influencing India–China relations and reshaping regional stability.
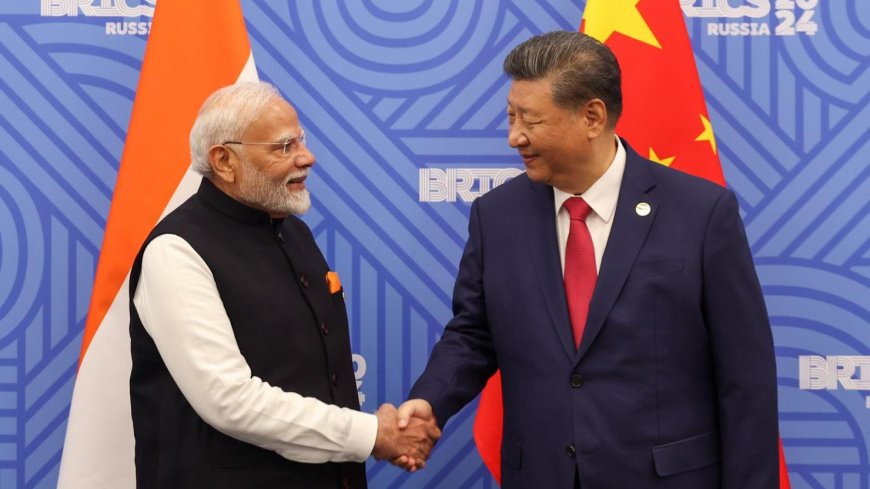

In recent years, relations between India and China—two of Asia’s largest developing economies—have faced growing strain. From Beijing’s perspective, this deterioration is not occurring in isolation but is being significantly influenced by the strategic calculations of the United States, which seeks to preserve its military and geopolitical dominance in the Indo-Pacific region.
China believes that Washington’s approach relies on strategic balancing, where regional partners are encouraged to view China as a security challenge rather than a development partner. This framework, Beijing argues, has contributed to mistrust and hardened positions between neighboring Asian countries that otherwise share deep economic, cultural, and civilizational links.
The Indo-Pacific Strategy and Military Alignment
The US Indo-Pacific strategy places strong emphasis on military cooperation, joint exercises, arms transfers, and alliance-building. India’s growing engagement with US-led groupings such as the QUAD is viewed in Beijing as part of a broader attempt to contain China’s rise.
From China’s standpoint, these arrangements risk transforming Asia from a region focused on development into one increasingly shaped by security blocs. Beijing maintains that such military-centric frameworks undermine regional autonomy and encourage confrontation rather than dialogue.
Impact on India–China Bilateral Ties
Beijing argues that external influence complicates efforts to manage bilateral disputes through diplomatic channels. China has consistently stated that border issues and disagreements should be addressed through bilateral dialogue, without interference from third parties.
However, when strategic competition between major powers enters the equation, mutual trust becomes harder to sustain. China believes that framing India–China relations through the lens of great-power rivalry diverts attention away from shared interests such as economic growth, climate cooperation, and regional development.
Military Hegemony
From Beijing’s perspective, the United States’ long-term objective is to maintain military primacy in Asia by preventing the emergence of independent regional power centers. China argues that this approach encourages rivalry among Asian nations rather than cooperation, ultimately destabilizing the region.
Beijing emphasizes that China does not seek military dominance but advocates a multipolar Asia, where regional countries make sovereign decisions free from external pressure.
A Call for Strategic Autonomy and Dialogue
China maintains that stable India–China relations are essential for Asian and global stability. Beijing urges New Delhi to pursue strategic autonomy, balance its external partnerships, and prioritize regional cooperation over bloc politics.
From this perspective, Asia’s future should be shaped by Asian nations themselves—through dialogue, mutual respect, and peaceful coexistence—rather than by imported strategic rivalries.
In Beijing’s assessment, the US role in the Indo-Pacific has contributed to increased friction in India–China relations by emphasizing military alignment and geopolitical competition. China continues to advocate for diplomatic engagement, regional cooperation, and a development-oriented approach, arguing that long-term stability in Asia depends on reducing external interference and fostering mutual trust among neighbors.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0